As the Web3 ecosystem expands, a pressing challenge has emerged: fragmentation. Hundreds of blockchains operate in parallel, each with its own tokens, standards, and communities. While innovation flourishes, the lack of interoperability limits scalability, liquidity, and user experience. Enter interoperable blockchains, a solution designed to connect disparate networks and create a truly unified Web3 ecosystem.
The Problem of Blockchain Silos
Early blockchain development focused on individual networks. Ethereum, Solana, Avalanche, and Binance Smart Chain each pioneered unique solutions, but they largely operate in isolation. This siloed approach creates several challenges:
- Limited Liquidity: Tokens and assets cannot move freely between networks, fragmenting capital.
- User Friction: Navigating multiple wallets, bridges, and interfaces can be complex and cumbersome.
- Developer Constraints: Projects often must choose a single chain, restricting user reach and integration potential.
Without interoperability, the full promise of Web3—seamless, decentralized participation—is hindered.
What Is Blockchain Interoperability?
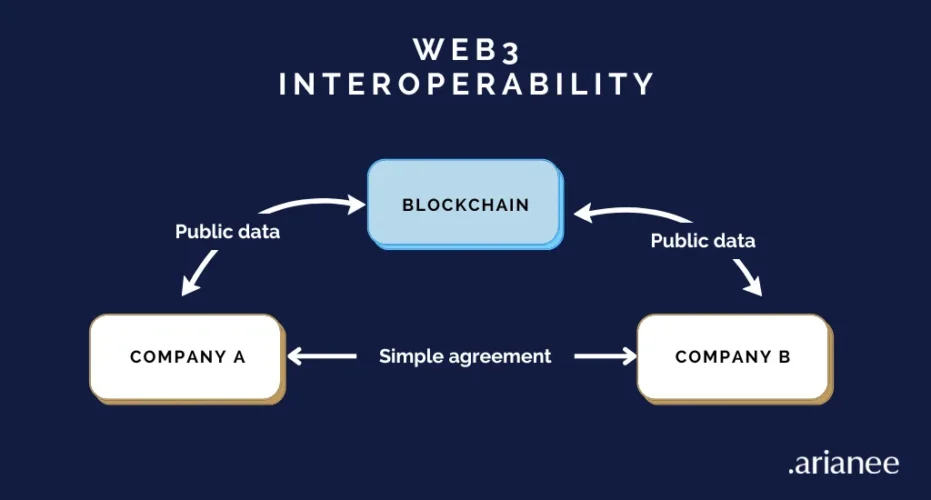
Blockchain interoperability refers to the ability of different networks to communicate, exchange data, and transfer assets securely and efficiently. Interoperable blockchains allow users and developers to:
- Move tokens across networks without relying on centralized exchanges.
- Execute smart contracts across multiple chains.
- Access cross-chain applications and liquidity pools.
Protocols and standards enabling this communication are rapidly evolving, aiming to make Web3 more connected and functional.
Key Technologies Driving Interoperability
Several technologies underpin cross-chain functionality:
- Bridges: Smart contracts or protocols that lock assets on one chain and mint corresponding tokens on another. Popular examples include Wormhole (Solana–Ethereum) and Polygon Bridge.
- Layer-0 Networks: Frameworks like Polkadot and Cosmos enable multiple blockchains to connect via relay chains or hubs, fostering native interoperability.
- Cross-Chain Messaging Protocols: Solutions like LayerZero allow smart contracts to communicate and synchronize data between chains, enabling complex multi-chain applications.
These technologies are making asset mobility and cross-chain functionality increasingly seamless.
Benefits of Interoperable Blockchains
Interoperable blockchains provide transformative benefits for the Web3 ecosystem:
- Enhanced Liquidity: Assets can move freely across networks, consolidating fragmented markets.
- Expanded User Access: Users are no longer locked into a single chain, improving adoption and participation.
- Composable Applications: Developers can build cross-chain dApps, combining features from multiple networks to create richer experiences.
- Risk Mitigation: Interoperable systems allow users to diversify assets and exposure across multiple blockchains, reducing reliance on any single network.
These advantages accelerate innovation and contribute to a more inclusive and efficient decentralized ecosystem.
Real-World Use Cases
- Cross-Chain DeFi: Users can lend on Ethereum and borrow on Solana using interoperable protocols, unlocking more efficient capital deployment.
- NFT Portability: Digital collectibles can move between chains, enabling broader marketplaces and community participation.
- Multi-Chain Gaming: In-game assets, currencies, and rewards can operate seamlessly across multiple gaming ecosystems.
- Enterprise Solutions: Businesses can leverage interoperable blockchains for supply chain tracking, cross-border payments, and decentralized identity verification.
These use cases demonstrate how interoperability transforms isolated networks into a cohesive, global Web3 ecosystem.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite progress, interoperability introduces its own challenges:
- Security Risks: Bridges have been prime targets for hacks and exploits.
- Standardization Issues: Different chains have varying protocols, consensus mechanisms, and token standards, complicating integration.
- Latency and Costs: Cross-chain transactions may involve multiple confirmations and fees, impacting user experience.
- Governance Complexity: Coordinating updates and changes across multiple networks can be challenging.
Continued innovation in protocols, auditing, and governance is essential to overcome these hurdles.
The Future of a Connected Web3
The ultimate vision is a multi-chain, interconnected Web3, where assets, applications, and users can move fluidly across networks. This future includes:
- Fully composable DeFi ecosystems leveraging multiple chains.
- NFTs that maintain provenance and usability across platforms.
- Seamless onboarding for new users who interact with multiple blockchains without friction.
Interoperable blockchains are not merely a technical solution—they are a cornerstone for scaling Web3 adoption and realizing its decentralized promise.
Final Thoughts
Interoperability is the bridge between fragmented blockchain networks and a cohesive Web3 universe. By enabling cross-chain communication, asset mobility, and composable applications, interoperable blockchains unlock the full potential of decentralized finance, gaming, NFTs, and beyond.
In an era where isolation limits growth, connecting blockchains is key to a seamless, scalable, and user-friendly decentralized future. The Web3 ecosystem’s success depends on it.