Decentralized finance, or DeFi, has emerged as one of the most transformative forces in the financial world. While traditional banking has long controlled lending, borrowing, and interest rates, DeFi is rewriting the rules—removing intermediaries, democratizing access, and creating a system where financial services are borderless, transparent, and programmable. In this article, we explore how DeFi lending and borrowing is challenging the conventional banking model and reshaping the future of finance.
The Traditional Lending Paradigm
Banks have historically served as the gatekeepers of credit. Individuals and businesses rely on banks to deposit funds, access loans, and earn interest. These institutions mediate between savers and borrowers, charging fees and interest spreads to generate profit.
While the model has proven effective, it comes with limitations:
- Accessibility Barriers: Credit approval often depends on credit scores, income verification, and geographic location.
- Centralized Control: Banks decide who qualifies for loans and under what terms.
- Slow Processes: Loan approvals, disbursements, and repayments can take days to weeks.
- Opaque Systems: Interest rates, collateral requirements, and fees can lack transparency.
DeFi is tackling these inefficiencies head-on.
Enter DeFi Lending and Borrowing
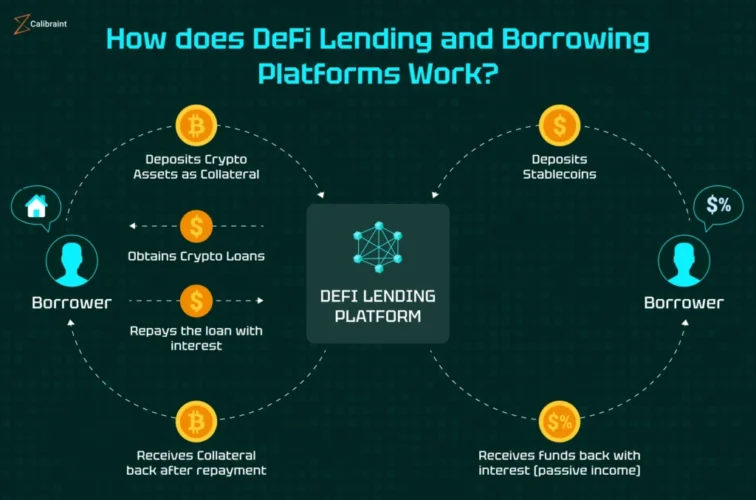
DeFi platforms leverage smart contracts—self-executing programs on blockchains—to automate lending and borrowing. By eliminating the middleman, DeFi enables peer-to-peer lending directly on-chain.
Key features include:
- Global Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection and compatible wallet can participate. There are no credit score checks or geographical restrictions.
- Automated Interest Rates: Rates are algorithmically determined based on supply and demand, ensuring real-time adjustments without human intervention.
- Transparent Collateralization: Borrowers often provide digital assets as collateral, fully visible on-chain. Smart contracts enforce rules, reducing counterparty risk.
Popular platforms such as Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO have pioneered these models, offering users the ability to lend tokens, earn yield, and borrow assets against collateral—all within a decentralized framework.
How DeFi is Democratizing Finance
The most profound impact of DeFi lending lies in financial inclusion. In many parts of the world, access to traditional banking is limited or non-existent. DeFi bridges this gap, allowing anyone to lend or borrow funds without intermediaries.
For example:
- A user in Southeast Asia can borrow stablecoins using crypto as collateral, gaining access to liquidity without a local bank.
- Investors worldwide can lend assets and earn interest rates higher than traditional savings accounts, diversifying their portfolio across decentralized protocols.
DeFi transforms users from passive customers into active participants in a global financial ecosystem.
Collateral, Over-Collateralization, and Risk Management
Unlike banks, which use credit scoring, DeFi primarily relies on over-collateralization. Borrowers must deposit more value than they intend to borrow, ensuring that lenders are protected against default.
For example, a borrower might lock $1,500 worth of Ethereum to borrow $1,000 in DAI stablecoins. If the collateral value drops below a predefined threshold, smart contracts automatically liquidate the collateral to protect lenders.
While this reduces credit risk, it introduces volatility risk, as crypto prices can fluctuate rapidly. Innovations like stablecoins, decentralized insurance, and multi-asset collateralization are emerging to address these challenges.
Yield Farming and Interest Rate Dynamics
DeFi lending platforms offer competitive interest rates thanks to dynamic algorithms. Supply and demand dictate the yield, which can fluctuate daily based on liquidity and market activity.
This has given rise to yield farming, where users strategically lend or borrow assets to maximize returns across multiple platforms. Unlike traditional fixed-interest banking, DeFi provides an environment where capital is fluid and performance-driven.
The result is a more meritocratic financial system: higher demand for certain assets naturally drives better returns for lenders and incentivizes efficient capital allocation.
Smart Contracts: Trustless and Transparent
The backbone of DeFi lending is smart contracts, which eliminate the need for trust in a centralized authority. Contracts execute automatically when conditions are met, enforcing loan terms, repayments, and liquidations.
This transparency not only reduces operational costs but also mitigates fraud and human error. Unlike traditional banking, where loan agreements may be opaque or subject to discretionary enforcement, DeFi ensures trustless compliance.
Risks and Considerations
While DeFi offers transformative potential, it carries inherent risks:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Coding bugs can be exploited, leading to losses.
- Market Volatility: Collateralized loans can be liquidated during rapid price swings.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: DeFi operates in a largely unregulated space, raising compliance concerns for large-scale adoption.
- User Responsibility: Unlike banks, there is no customer support or recourse for lost funds or failed transactions.
Investors must weigh potential rewards against these risks and consider diversification, audits, and platform reputation when participating.
Real-World Implications and Adoption
DeFi lending is no longer theoretical. Institutional players, hedge funds, and even corporations are experimenting with decentralized credit protocols. The benefits are clear: faster transactions, programmable contracts, and global accessibility.
Emerging innovations include:
- Flash Loans: Instant, uncollateralized loans that must be repaid within a single transaction block.
- Multi-Collateral Loans: Borrowing against diverse crypto assets to minimize volatility risk.
- Decentralized Credit Scoring: On-chain reputation systems that allow uncollateralized borrowing in the future.
These innovations hint at a world where traditional finance and DeFi may coexist, complementing one another rather than competing exclusively.
Final Thoughts: The New Financial Frontier
DeFi lending and borrowing is more than a technological shift—it’s a paradigm shift in how financial services are delivered. By leveraging blockchain, smart contracts, and tokenized assets, DeFi removes barriers, democratizes access, and challenges the conventional banking model.
While risks remain, the growth of platforms, institutional interest, and user adoption signals that decentralized credit systems are here to stay. In this new financial frontier, anyone with crypto can become a lender, a borrower, or both, participating in a borderless, trustless economy.
The future of finance is decentralized, programmable, and inclusive—and lending and borrowing are leading the charge.