Decentralized finance (DeFi) has evolved far beyond simple token swaps and lending platforms. A new frontier in this space is synthetic assets and derivatives, which replicate the value of real-world or digital assets, enabling users to gain exposure to a wide range of markets without holding the underlying asset. These instruments are driving the growing complexity—and sophistication—of the DeFi ecosystem.
What Are Synthetic Assets?
Synthetic assets, or “synths,” are blockchain-based tokens designed to mirror the value of other assets, including fiat currencies, stocks, commodities, or cryptocurrencies. They achieve this through smart contracts, which lock collateral and algorithmically maintain the asset’s price parity.
For example:
- A user could mint a synthetic token representing Tesla stock or gold without directly purchasing the real-world asset.
- These tokens can be traded, borrowed, or used in DeFi strategies, effectively opening access to markets that were traditionally restricted or centralized.
Platforms like Synthetix have pioneered this model, allowing users to trade synths with global accessibility and without intermediaries.
How Derivatives Fit Into DeFi
Derivatives in DeFi are financial contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset. This includes instruments like futures, options, and perpetual swaps. Unlike traditional derivatives, DeFi derivatives are:
- Non-custodial: Users retain control of collateral and funds.
- Permissionless: Anyone can participate without intermediaries or brokers.
- Programmable: Smart contracts automatically enforce contract terms, including settlement and liquidation.
By combining derivatives with synthetic assets, DeFi enables complex strategies such as hedging, speculation, and yield optimization on-chain.
Benefits of Synthetic Assets and Derivatives
- Global Market Access: Users can gain exposure to traditional financial markets without geographic or regulatory barriers.
- Capital Efficiency: Synthetic positions require collateral rather than full asset ownership, allowing leverage and more flexible capital allocation.
- Decentralization and Transparency: All transactions are recorded on-chain, providing verifiable ownership and reducing reliance on centralized institutions.
- Programmable Financial Innovation: Developers can create novel derivatives, yield strategies, or automated investment protocols without traditional intermediaries.
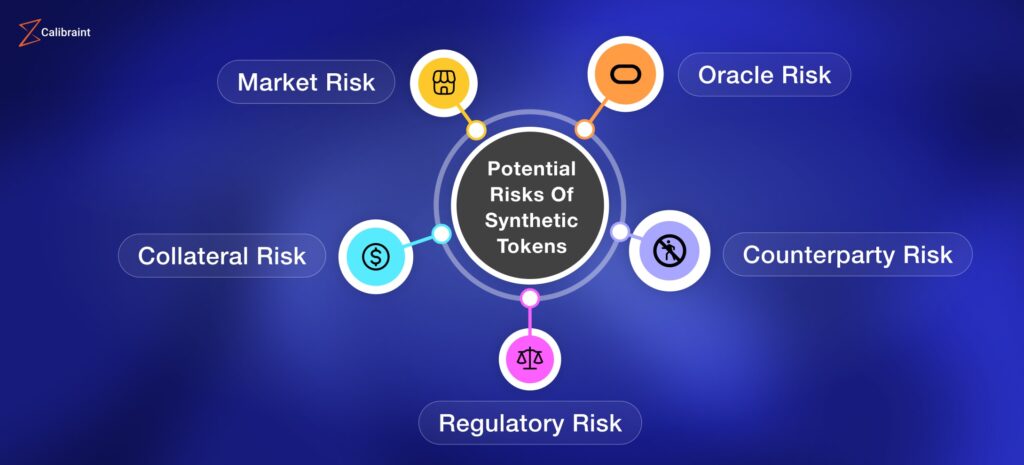
Risks and Considerations
While synthetic assets and derivatives unlock new opportunities, they introduce additional complexity and risk:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Coding errors or exploits can result in loss of funds.
- Price Oracles Dependency: Accurate asset pricing relies on oracles; manipulation can affect synthetic asset value.
- Leverage Risk: Using collateral for derivatives can magnify losses during market volatility.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Synthetic derivatives mimic regulated financial instruments, raising potential compliance issues.
Participants must carefully assess collateralization, platform security, and protocol governance before engaging in synthetic markets.
Real-World Implications
The introduction of synthetic assets and derivatives expands DeFi’s reach beyond cryptocurrencies. Users can now:
- Hedge against crypto volatility by holding stablecoin-based synths.
- Gain exposure to stock indices or commodities directly on-chain.
- Participate in complex trading strategies that were previously limited to institutional investors.
This evolution transforms DeFi into a full-featured financial ecosystem, capable of competing with traditional finance while remaining accessible and decentralized.
The Future of DeFi Complexity
As platforms refine synthetic assets and derivative protocols, expect:
- Cross-Chain Synths: Interoperable synthetic assets operating across multiple blockchains.
- More Robust Risk Management: Enhanced collateral models, insurance, and automated liquidation mechanisms.
- Integration with NFTs and DeFi Services: Using synthetic assets for NFT-backed loans, yield farming, or tokenized real-world assets.
The growing sophistication signals a maturing DeFi landscape, where advanced financial instruments coexist with accessible, decentralized protocols.
Final Thoughts
Synthetic assets and derivatives exemplify DeFi’s potential to replicate—and in some cases improve—traditional financial services on-chain. They offer access, flexibility, and programmability while challenging centralized finance paradigms.
While complexity and risk increase, the opportunities for innovation, global participation, and decentralized financial growth are unparalleled. In the world of DeFi, synthetic assets and derivatives are both a tool and a symbol of the ecosystem’s evolving maturity.